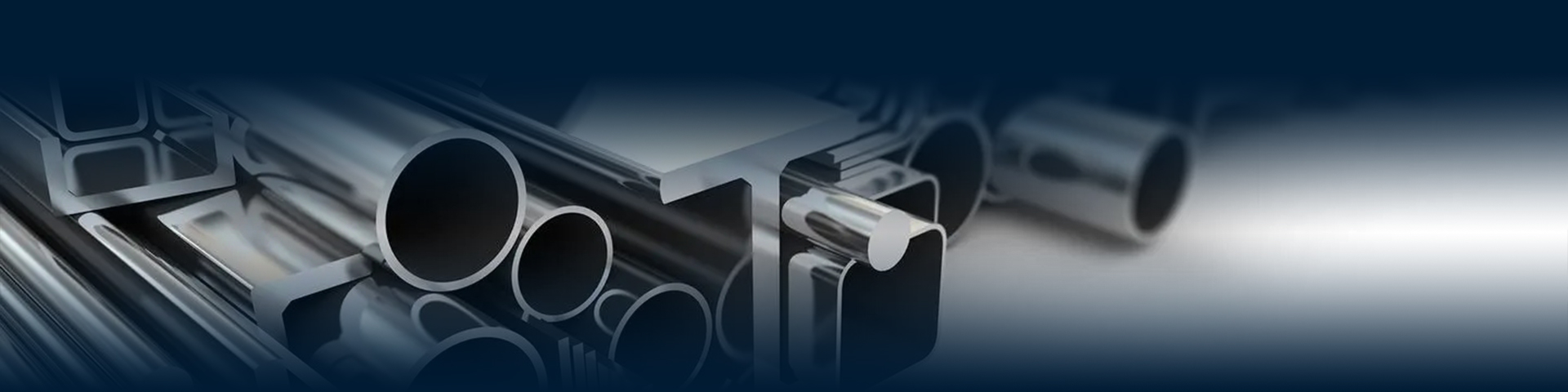
Galvanized steel is an alloy material with a layer of zinc coating on the surface of steel, mainly used for anti-corrosion protection. Its characteristics are mainly manifested in the following aspects:
Corrosion resistance: Zinc has a more active chemical property than steel. Therefore, when galvanized steel is exposed to air, zinc will react with oxygen in the air first to form a dense oxide zinc film, which prevents the steel from being further oxidized. This characteristic makes galvanized steel have excellent corrosion resistance and can resist the erosion of harsh environments such as moisture, acidity, and alkalinity for a long time.
Durability: Due to its corrosion resistance, galvanized steel usually has a longer service life than ungalvanized steel. It can maintain good performance and appearance even if exposed to various climatic conditions outdoors for a long time.

Aesthetics: Galvanized steel has a smooth surface and uniform color, which has a certain decorative effect. In addition, different surface effects, such as matte, gloss, and patterns, can be obtained through different processing techniques to meet different decorative needs.
Processability: Galvanized steel has good processing performance and can be processed through various techniques such as cutting, bending, and welding, which is convenient for making components of various shapes and sizes.
Environmental protection: Zinc is a recyclable material, so galvanized steel can be recycled and reused after scrapping, reducing environmental pollution. At the same time, the galvanizing process itself also meets environmental protection requirements and does not produce harmful substances.
Cost-effectiveness: Although the initial cost of galvanized steel may be slightly higher than that of ungalvanized steel, its cost-effectiveness is usually higher due to its longer service life and lower maintenance cost.
It should be noted that although galvanized steel has many advantages, additional anti-corrosion measures may be required in some special environments (such as high-temperature, high-humidity, and high-corrosion environments). In addition, care should be taken to avoid damaging the zinc coating during processing and installation to ensure its anti-corrosion performance.