Possible Quality Issues and Their Causes of Hot-dip Galvanized Steel Sheets
Taking into account the production process and packaging of hot-dip galvanized steel sheets, there may be some surface defects as follows:
(1) Defects of original sheet
Surface defects on the original sheet, such as creases, pits, and wavy edges, will all affect the galvanized sheet and become its surface defects. Therefore, before production, manufacturers must inspect the original sheet.
(2) Black spots
a. If the purity of the galvanized layer is not enough, metal impurities will form a galvanic cell on the zinc surface. When it is favorable for hydrogen evolution, it is easy to produce black spots on the surface of the zinc layer.
b. When the content of impurities such as copper, iron, and arsenic in the galvanized layer is high, these impurities will appear black after passivation treatment.
c. Insufficient treatment of dirt and corrosion on the original sheet surface will form residues, causing some parts to fail to be galvanized, leading to defects in the galvanized layer and easy to fall off, resulting in black spots.
d. Missed galvanizing during galvanizing is prone to forming black spots during post-processing.
e. Residues or small black ashes (carbon or carbon compounds) in the galvanizing solution adhere to the surface of the zinc layer or reside inside the zinc layer, firmly bonded to the zinc layer. Black spots can be seen on the finished galvanized sheet.
f. Abrasion black spots. Caused by rough handling during transportation and storage.
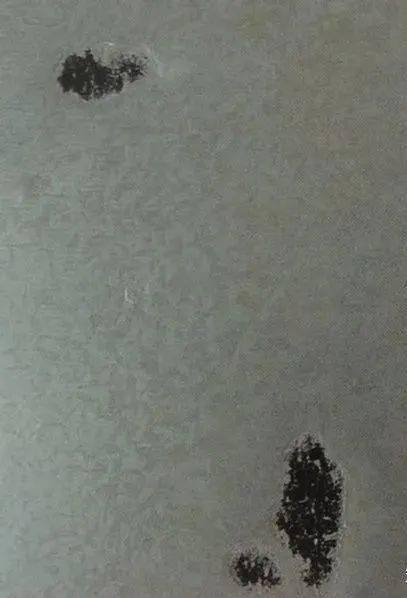

(3) White rust
When the surface of the galvanized steel sheet is dampened or rained into, zinc is oxidized at a certain temperature, producing white powder. The corrosion resistance of the surface with white rust is greatly reduced, affecting its use.
(4) Uneven galvanized layer
The surface of the galvanized sheet has uneven zinc layers, uneven thickness, and even small particles on the surface. There is excess zinc liquid on the surface of the strip steel coming out of the galvanizing pot, and these excess zinc liquids are blown off with a gas knife (spraying high-pressure gas) to control the thickness of the zinc layer. The gas pressure of the gas knife, the spacing between the gas knife and the strip steel, and the speed of the strip steel will directly affect the thickness of the zinc layer. If the gas supply of the gas knife is unstable or the gas knife pressure is insufficient, it will cause the galvanized layer to accumulate, forming zinc scars.
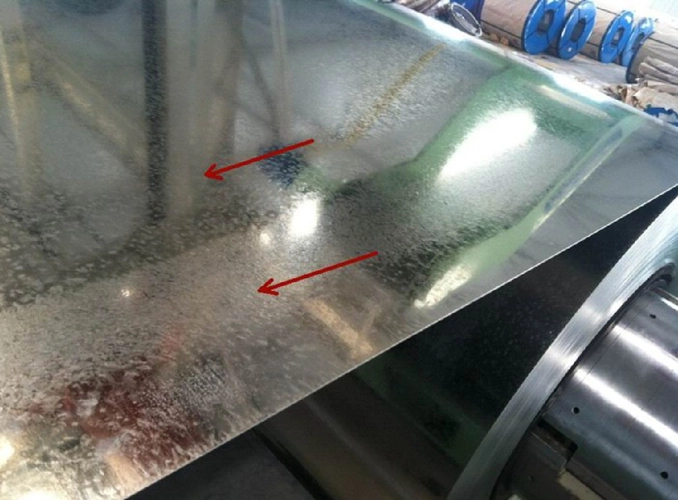

(5) Slag inclusion
Residuals or dross (metal or non-metal inclusions) exist in the galvanizing solution, and sometimes these inclusions are mixed into the galvanized layer, causing small round spots on the surface of the sheet, and even making the original sheet unable to adhere to zinc, easily causing exposed iron points.
(6) Scratches and abrasions, etc.
When the galvanized coil is passed through the tension straightener, foreign objects in the straightener cause surface scratches, abrasions, etc.
(7) Chromic acid dirt
To improve the corrosion resistance of the galvanized steel sheet, a very thin passivation layer is formed on the surface of the strip steel, which can be achieved by chromic acid treatment, namely chromating treatment. However, if the chromic acid treatment is not done properly and there is residual liquid, a light yellow band or stain, or even black spots, may appear on the surface of the galvanized sheet.